Among the exciting renewable energy solutions, Hydrogen shines as a versatile element with incredible potential to lead us towards a future with zero emissions.
In this blog post, we’ll dive into the exciting world of hydrogen and its various forms, exploring how it can revolutionize the energy landscape.
What is Hydrogen, and where does it occur?
Hydrogen, the universe’s foremost and most essential element, comprises a positively charged proton and a negatively charged electron. It boasts the lowest atomic weight among all elements and is typically a colorless and odorless gas under standard conditions.
Fuel of the future?
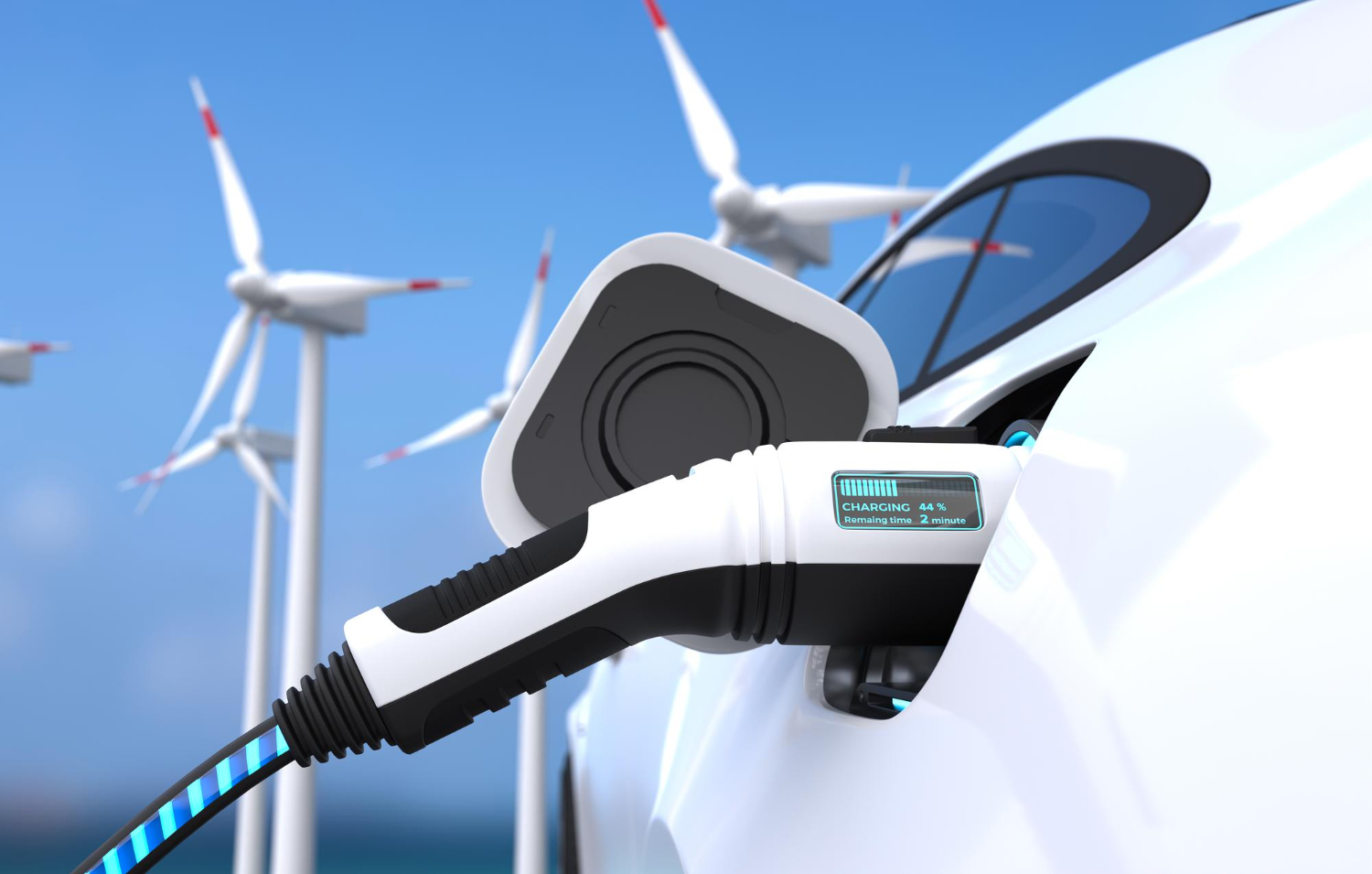
One of the most intriguing applications of hydrogen involves its use in the field of transportation. Hydrogen can be efficiently stored and moved either as a liquid or gas, thanks to its high energy concentration. This characteristic makes it an excellent candidate for powering both vehicles and industrial machinery.
Hydrogen Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles (FCEVs), encompassing cars and buses, represent an exciting innovation in this context. These vehicles run on electricity and release only water vapor as a byproduct. Instead of depending on traditional batteries, they store energy as compressed hydrogen fuel. The fuel cells within these vehicles then transform this compressed hydrogen into electricity, which powers the electric motor and provides a range similar to that of conventional vehicles using gasoline or diesel. Additionally, refueling hydrogen-powered vehicles is a speedy process, taking just a few minutes.

Different types of Hydrogen: Blue, Green, and Grey
- Blue Hydrogen: This form of hydrogen is crafted from natural gas and then undergoes decarbonization using carbon capture and storage techniques, transforming it into an eco-friendlier option compared to grey hydrogen.
- Green Hydrogen: Green hydrogen comes to life through the process of electrolysis, where water is split using electricity harnessed exclusively from sustainable sources like wind or solar energy. It shines as a symbol of sustainability and eco-consciousness.
- Grey Hydrogen: Grey hydrogen is produced using energy derived from hydrocarbons, especially natural gas. Although it falls short of the environmental friendliness of green hydrogen, it still presents advantages over conventional fossil fuels.
Hydrogen Production: The Green Route
While hydrogen is abundant, it’s rarely found in its pure form in nature and requires the use of different chemical reactions for production.
Presently, most of the hydrogen is manufactured through a process called fossil fuel reforming. This method involves the reaction of natural gas with steam. However, there’s a more environmentally friendly approach that revolves around producing hydrogen from sustainable sources. This can be achieved, for instance, by using electrolysis, which splits water into hydrogen and oxygen using electricity generated by wind or solar power.
To produce hydrogen, various primary energy sources can be utilized, including:
- Biogas
- Natural gas
- Solar energy
- Wind power
These energy sources can undergo processes like steam methane reforming (SMR) or electrolysis to yield hydrogen, which then becomes a valuable product in the energy landscape.
Safety at the Core of Hydrogen Energy
Hydrogen-powered vehicles maintain the same level of safety as conventional vehicles. Hydrogen has been employed safely for many years in numerous chemical processes and within the heavy industry sector. Just like any energy source, be it traditional or innovative, it’s essential to handle flammable fuels with care.
Hydrogen storage and fuel cell technologies have undergone thorough and exhaustive testing procedures to guarantee their safety. Moreover, precise safety standards have been established for hydrogen refueling technologies and vehicles.